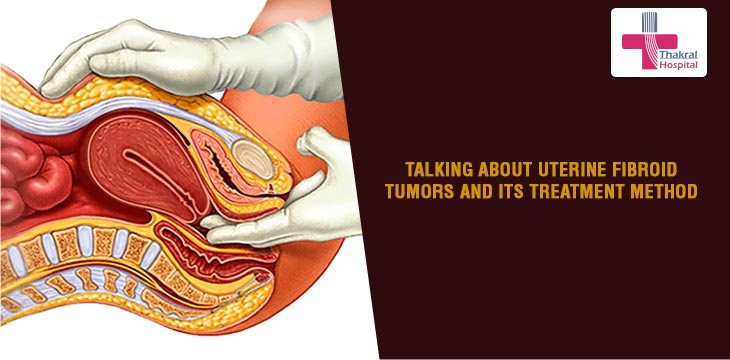
Talking About Uterine Fibroid Tumors And Its Treatment Method
The frequency of uterine fibroid tumors progresses as women grow more older, and they may be seen in more than 30 % of women aging between 40 to 60 years of age. Risk agents constitute nulliparity, obesity, relationship history, black race, and hypertension. Many tumors are asymptomatic and may be diagnosed unexpectedly. Although a causal link has not been authenticated, fibroid tumors are connected with menorrhagia, pelvic discomfort, pelvic or urinary obstructive signs, infertility, and productivity loss. Transvaginal ultrasonography, magnetic resonance imaging, sonohysterography, and hysteroscopy are done to assess the size and location of tumors.
Ultrasonography is the most preferred should be used first because it is the least invasive and most cost-effective research. Surgery options involve hysterectomy, myomectomy, uterine artery embolization, myolysis, and medical treatment. Medication must be individualized based on such concerns as the presence and sharpness of symptoms, the patient’s hope for comprehensive operation, the desire to conserve childbearing potential, the value of uterine protection, infertility related to uterine cavity distortions, and previous pregnancy complexities linked to fibroid tumors.
Non-Surgical Remedies For Fibroid Tumors
Drugs can help control fibroid-related traits. The most useful pills for the treatment of fibroids are gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (GnRHa), GnRH agonists induce low-estrogen menopause-like state which provokes the reduction area of the tumor and uterus. Uterine size has been confirmed to decline around 50 percent after three months of therapy with these medicines. GnRH agonists also check the menstrual flow, enabling women with bleeding-induced anemia to raise their iron stores.
Regrettably, long-duration use of GnRH agonists can guide to bone loss, nevertheless when GnRH agonist medication is stopped it is accompanied by a speedy regrowth of the fibroids and the uterus to pre-treatment dimensions. Therefore, the use of GnRH agonists solely for the treatment of fibroids is frequently limited to a small period of one to three-month preoperative sequence to contract the uterus in development for surgery or to correct anemia before an operation. Other medical treatments including androgenic agents, progestins, depomedroxyprogesterone acetate, etc.
Oral preventative pills have been utilized to control menorrhagia or profuse blood flow in women with leiomyomas, likely by diminishing the endometrium. Tranexamic acid is an anti-fibrinolytic pill that does not comprise hormones that can also be practiced to treat massive bleeding. None of these medicines reduce uterus or fibroid volume.
Uterine Fibroid Embolization
Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE), also recognized as uterine artery embolization (UAE) is a choice to surgery that requires placing a catheter through a small incision in the groin into an artery in the leg and controlling the catheter via x-ray pictures to the arteries of the uterus. Once there, the catheter is applied to deliver agents that block off the blood vessels that supply the uterine fibroids. Total radiation presentation during this mode is analogous to that in one to two CT scans.
Uterine artery embolization (UAE) does not eliminate uterine fibroids, but prompts them to shrink by 30 to 50 percent. The benefits of this method include no abdominal surgeries and shorter recuperation time. After this procedure, women may encounter amenorrhea depending on their age. Fibroids can reappear or revascularize after this method, and up to 20 percent of women inquire additional treatments in the five years following UAE.
Focused Ultrasound Treatment
MRI-guided concentrated ultrasound (FUS) is a noninvasive method choice for uterine fibroids that damages fibroids while protecting the normal uterus. Focused high-frequency, high-energy sound waves are applied to hit the proteins in fibroids until they are damaged or killed. Used in union with MRI, FUS enables doctors to accurately target and monitor treatment. A single therapy gathering lasts roughly 3 hours. Although fibroids are reviewed and ultimately diminish in size, they are not eliminated. Women can continue normal activity within a day of the method, however, the long-term effectiveness of this procedure is not recognized and it is not advised for women who require to preserve their fertility.
Reference
Fibroids are commonly seen in aging women but needs proper treatment from a qualified physician. Try meeting Dr. Neeru Thakral, the best gynae laparoscopic surgeon in Gurgaon.
REACH US :
Name : Thakral Hospital and Fertility Centre – IVF Centre in Gurgaon
Address : 316 / 16, Sohna Alwar Road, Behind Petrol Pump, Shivaji Nagar,
Sector 11, Gurugram, Haryana 122001
Phone : 09971239503
Website : https://www.thakralhospital.com/
One thought on “Talking About Uterine Fibroid Tumors And Its Treatment Method”
Nice Information